untung99.homes: Set up a Git repository
Untung99 menawarkan beragam permainan yang menarik, termasuk slot online, poker, roulette, blackjack, dan taruhan olahraga langsung. Dengan koleksi permainan yang lengkap dan terus diperbarui, pemain memiliki banyak pilihan untuk menjaga kegembiraan mereka. Selain itu, Untung99 juga menyediakan bonus dan promosi menarik yang meningkatkan peluang kemenangan dan memberikan nilai tambah kepada pemain.
Berikut adalah artikel atau berita tentang Harian untung99.homes dengan judul untung99.homes: Set up a Git repository yang telah tayang di untung99.homes terimakasih telah menyimak. Bila ada masukan atau komplain mengenai artikel berikut silahkan hubungi email kami di koresponden@untung99.homes, Terimakasih.
When you clone an existing Git repository, or put an existing project under Git version control, IntelliJ IDEA automatically detects if Git is installed on your computer. If the IDE can’t locate a Git executable, it suggests downloading it.
IntelliJ IDEA supports Git from the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2), which is available in Windows 10 version 2004.
If Git is not installed on Windows, IntelliJ IDEA searches for Git in WSL and uses it from there. Also, IntelliJ IDEA automatically switches to Git from WSL for projects that are opened when you use the \\wsl$ path.
If you need to manually configure IntelliJ IDEA to use Git from WSL, go to the Version Control | Git page of the IDE settings Ctrl+Alt+S, click the Browse icon in the Path to Git executable field and select Git from WSL via the \wsl$ path, for example, \\wsl$\debian\usr\bin\git.
Check out a project from a remote host (clone)
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to check out (in Git terms clone) an existing repository and create a new project based on the data you’ve downloaded.
-
In the Get from Version Control dialog, specify the URL of the remote repository you want to clone, or select one of the VCS hosting services on the left.
If you are already logged in to the selected hosting service, completion will suggest the list of available repositories that you can clone.

-
Click Clone. If you want to create a project based on the sources you have cloned, click Yes in the confirmation dialog. Git root mapping will be automatically set to the project root directory.
If your project contains submodules, they will also be cloned and automatically registered as project roots.
-
When you import or clone a project for the first time, IntelliJ IDEA analyzes it. If the IDE detects more than one configuration (for example, Eclipse and Gradle), it prompts you to select which configuration you want to use.
Select the necessary configuration and click OK.

The IDE pre-configures the project according to your choice. For example, if you select Gradle, IntelliJ IDEA executes its build scripts, loads dependencies, and so on.
Put an existing project under Git version control
You can create a local Git repository based on the existing project sources.
Associate the entire project with a single Git repository
-
Open the project that you want to put under Git.
-
Press Alt+` to open the VCS Operations Popup and select Enable Version Control Integration.
-
Choose Git as the version control system and click OK.
The entire project then will be associated with a single Git directory, so there is no need to add each file to the Git directory individually.
-
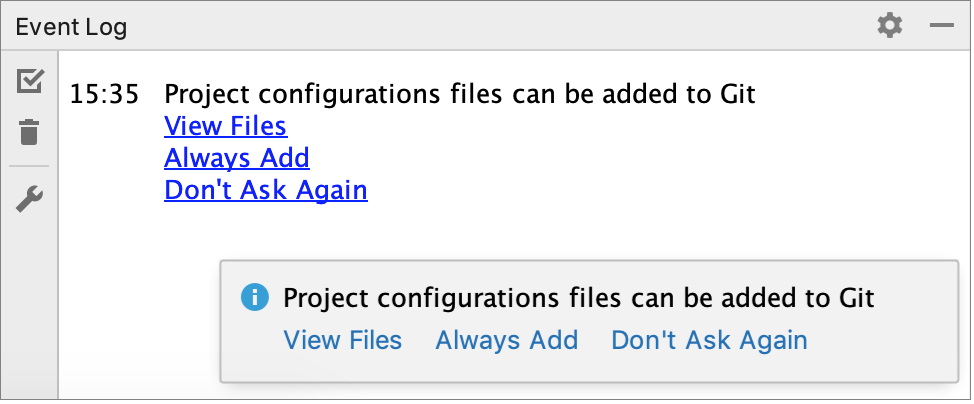
After VCS integration is enabled, IntelliJ IDEA will ask you whether you want to share project settings files via VCS. You can choose Always Add to synchronize project settings with other repository users who work with IntelliJ IDEA.
Associate different directories within the project with different Git repositories
-
Open the project that you want to put under Git.
-
In the dialog that opens, specify the directory where a new Git repository will be created.
Git does not support external paths, so if you choose a directory that is outside your project root, make sure that the folder where the repository is going to be created also contains the project root.
-
If you are creating multiple Git repositories inside the project structure, repeat the previous steps for each directory.
After you have initialized a Git repository for your project, you need to add project files to the repository.
Add files to the local repository
-
In the Commit tool window Alt+0, expand the Unversioned Files node.
-
Select the files you want to add to Git or the entire changelist and press Ctrl+Alt+A or choose Add to VCS from the context menu.
You can also add files to your local Git repository from the Project tool window: select the files you want to add, and press Ctrl+Alt+A or choose Git | Add from the context menu.
When Git integration is enabled in your project, IntelliJ IDEA suggests adding each newly created file under Git, even if it was added from outside IntelliJ IDEA. You can change this behavior in the Version Control | Confirmation page of the IDE settings Ctrl+Alt+S. If you want certain files to always remain unversioned, you can ignore them.
Sometimes you may need to leave certain files unversioned. These can be VCS administration files, artifacts of utilities, backup copies, and so on. You can ignore files through IntelliJ IDEA, and the IDE will not suggest adding them to Git and will highlight them as ignored.
You can only ignore unversioned files, that is files that you see in the Unversioned Files changelist. If a file is added to Git but not committed, you can right-click it in the Local Changes view and choose Rollback.
-
.git/info/exclude file.
Patterns listed in this file only apply to the local copy of the repository.
This file is created automatically when you initialize or check out a Git repository.
-
One or more .gitignore files in the VCS root directory and its subdirectories.
These files are checked into the repository so that the ignore patterns in them are available to the entire team. Therefore, it is a most common place to store the ignored file patterns.
-
Decide what kind of Git configuration file you are going to use to ignore files. If in doubt, use .gitignore.
-
Locate the unversioned file or folder you want to ignore in the Local Changes view or in Project tool window. File colors in these views help you identify the status of the file.
-
Right click the selection and choose Git | Add to .gitignore or Git | Add to .git/info/exclude.
File colors in these views help you identify the status of the file.
If you need to exclude files by a certain pattern, or files of a certain type, you can edit the .gitignore or .git/info/exclude file directly. See .gitignore patterns format.
Check project status
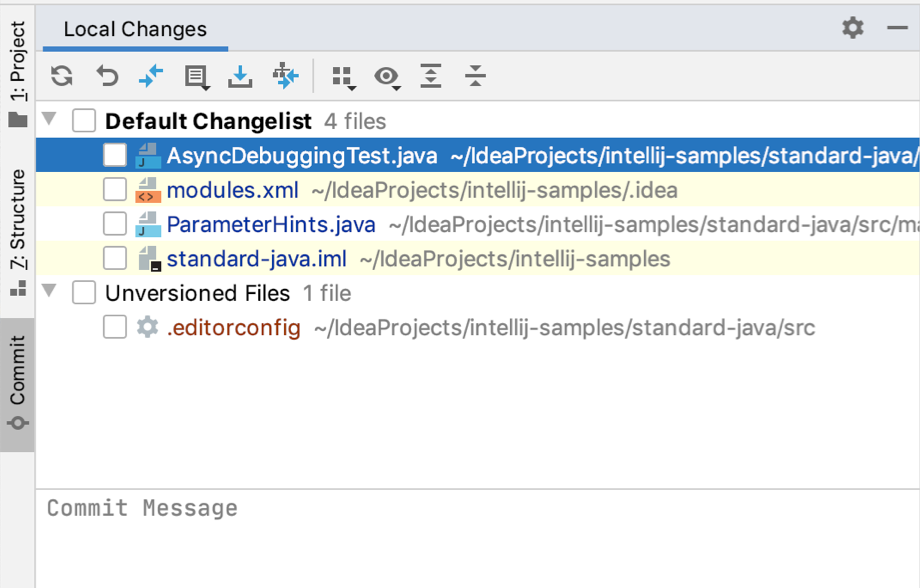
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to check the status of your local working copy compared to the repository version of the project. It uses specific colors to let you see which files have been modified, which new files have been added to the VCS, and which files are not being tracked by Git.
Open the Local Changes view.
-
The Changes changelist shows all files that have been modified since you last synchronized with the remote repository (highlighted in blue), and all new files that have been added to the VCS but have not been committed yet (highlighted in green).
-
The Unversioned Files changelist shows all files that have been added to your project, but that are not being tracked by Git.
For more info on changelists, see Group changes into different changelists.
Track changes to a file in the editor
You can also track changes to a file as you modify it in the editor. All changes are highlighted with change markers that appear in the gutter next to the modified lines, and show the type of changes introduced since you last synchronized with the repository. When you commit changes to the repository, change markers disappear.
The changes you introduce to the text are color-coded:
-
line added.
-
line changed.
-
line deleted.
You can manage changes using a toolbar that appears when you hover the mouse cursor over a change marker and then click it. The toolbar is displayed together with a frame showing the previous contents of the modified line:
You can roll back changes by clicking and explore the differences between the current and the repository version of the current line by clicking . To highlight the fragments that were changed, click .
Instead of reverting the whole file, you can copy any part of the contents of this popup and paste it into the editor.
Add a remote repository
If you created a Git repository based on local sources, you need to add a remote repository to be able to collaborate on your Git project, as well as to eliminate the risks of storing all of your codebase locally. You push changes to a remote repository when you need to share your work and pull data from it to integrate changes made by other contributors into your local repository version.
If you have cloned a remote Git repository, for example from GitHub, the remote is configured automatically and you do not have to specify it when you want to sync with it. The default name Git gives to the remote you've cloned from is origin.
For information on how to share project settings for different project formats, see Share project settings through VCS.
Define a remote
-
Create an empty repository on any Git hosting, such as Bitbucket or GitHub. You can create a repository on GitHub without leaving IntelliJ IDEA: see Share a project on GitHub.
-
If you haven't added any remotes so far, the Define remote link will appear instead of a remote name. Click it to add a remote.
-
In the dialog that opens, specify the remote name and the URL where it will be hosted, and click OK.
Add a second remote
In some cases, you also need to add a second remote repository. This may be useful, for example, if you have cloned a repository that you do not have write access to, and you are going to push changes to your own fork of the original project. Another common scenario is that you have cloned your own repository that is somebody else's project fork, and you need to synchronize with the original project and fetch changes from it.
-
Click the Add button on the toolbar or press Alt+Insert.
-
In the dialog that opens, specify the remote name and URL and click OK.
Learn more from this video:
Last modified: 30 March 2023